
In the early stages of Earth’s formation, the atmosphere was primarily composed of carbon dioxide (CO2), along with other gases like nitrogen and water vapor. This CO2-rich atmosphere played a crucial role in the development of life on Earth. The greenhouse effect, caused by CO2 and other greenhouse gases, trapped heat from the sun, keeping the planet warm enough for liquid to exist and for life to emerge.
What are Greenhouse Gases and its sources? An Overview
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are a group of gases that trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. These gases are naturally present in the atmosphere, but human activities have increased their concentrations, leading to global warming. Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are emitted from various natural and human-caused sources. Natural sources include volcanic eruptions and plant respiration, while human-caused sources include burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and agricultural practices. Understanding the sources of greenhouse gas emissions is crucial for addressing the issue.
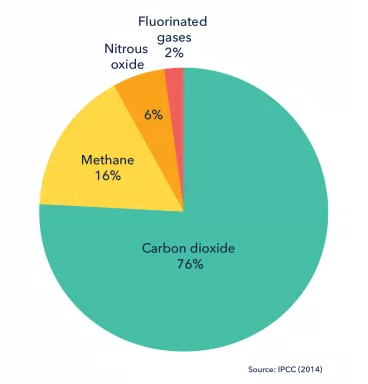
According to the Kyoto Protocol and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the primary greenhouse gases are:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Methane (CH4)
- Nitrous oxide (N2O)
- Fluorinated gases (F-gases)
The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
The greenhouse effect is a natural process by which greenhouse gases, such as CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide, trap heat in the atmosphere, keeping Earth warm enough to support life. However, human activities, primarily burning fossil fuels, have significantly increased greenhouse gas concentrations, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming
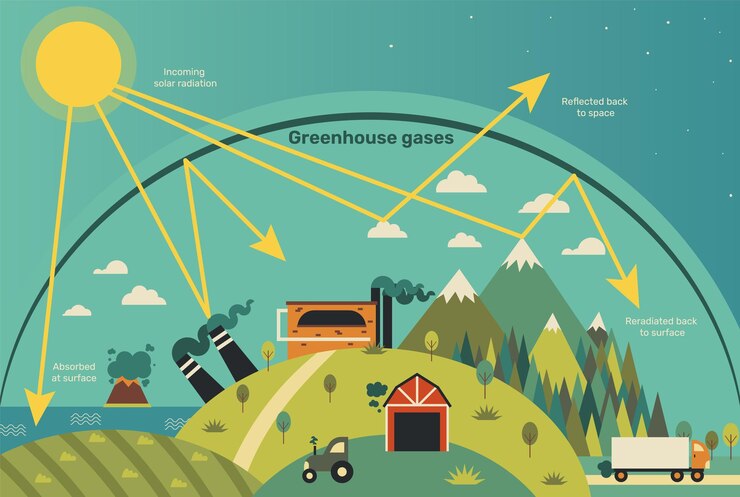
The Role of Greenhouse Gases in Our Climate
CO2 plays a critical role in maintaining Earth’s habitable temperature. Without CO2, Earth would likely plunge into an ice age, as heat would escape back into space. However, excessive CO2 levels can lead to a runaway greenhouse effect, causing the planet to overheat and become inhospitable to life.
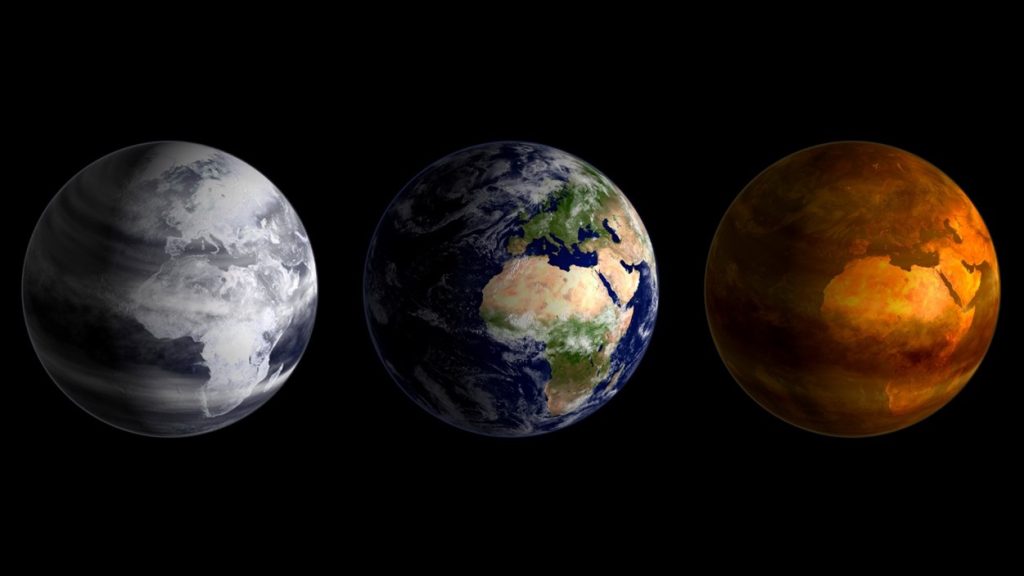

CO2 plays a critical role in maintaining Earth’s habitable temperature. Without CO2, Earth would likely plunge into an ice age, as heat would escape back into space. However, excessive CO2 levels can lead to a runaway greenhouse effect, causing the planet to overheat and become inhospitable to life.
Pre-Industrial CO2 Concentrations and Rising CO2 Levels & Temperature Trends
Before the Industrial Revolution, atmospheric CO2 concentrations were around 280 parts per million (ppm), a threshold for a stable climate. Exceeding this threshold leads to an increased risk of climate change impacts. It’s crucial to understand the historical context of greenhouse gas levels.
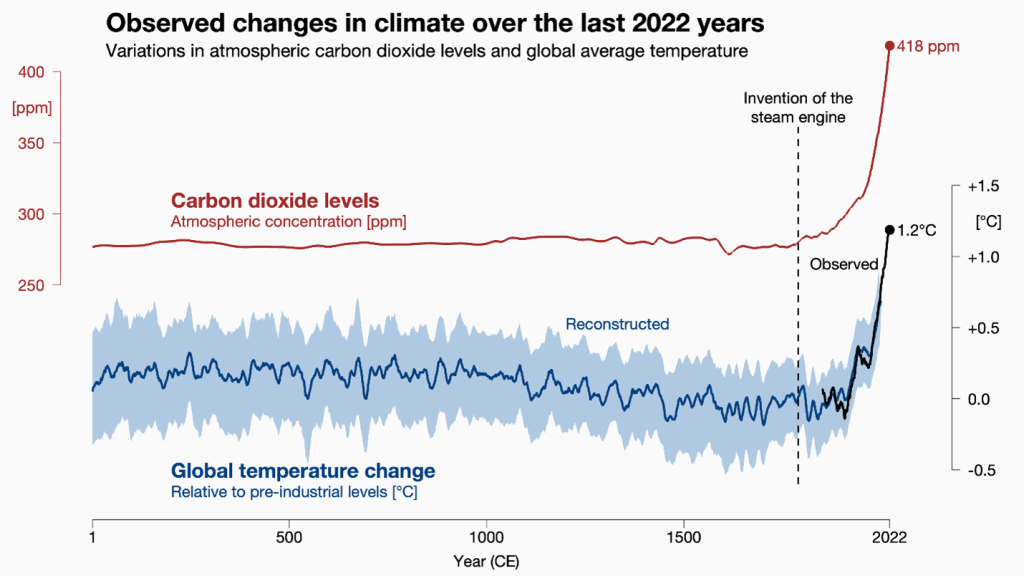
Since the Industrial Revolution, CO2 concentrations have risen dramatically over 50%, reaching 421 ppm in 2022. This increase coincides with a rise in global average temperatures of about 1 degree Celsius (1.8 degrees Fahrenheit). The correlation between rising CO2 levels and temperature trends is a significant concern.
Consequences of Exceeding CO2 Thresholds and Greenhouse Gas Emission Solutions
If CO2 emissions continue steadfast, atmospheric CO2 concentrations could exceed 500 ppm by the end of the century. This would lead to further warming, causing more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems. Understanding the consequences of exceeding CO2 thresholds is vital, as is exploring solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Impacts on Carbon Sequestration and the Path Forward
Excessive CO2 emissions can overwhelm Earth’s natural carbon sequestration processes, such as photosynthesis and ocean absorption. This imbalance further contributes to rising CO2 levels and exacerbates climate change. To mitigate climate change and its impacts, we must drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This requires a global transition to renewable energy sources, improved energy efficiency, and sustainable land-use practices including carbon offset programs and individuals’ behavioral changes on daily routine.
In conclusion, understanding greenhouse gases, their sources, and their impacts on our planet is vital for addressing the global challenge of climate change. By taking action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and implementing sustainable practices, we can work towards a more stable and habitable future for Earth.
To arrange a chat with one of our GHG reporting and reduction specialists to take a step on your organizational climate action, contact us at +974-44427968 or you may get in touch at: [email protected].
Author
Akash Boopathi
A Sustainability Professional with 3+ years of experience in the AEC industry. Industry oriented Skills in Sustainability planning, framework implementation, and Compliance monitoring with Voluntary and regulatory standards. In a mission contributing to a greener and resilient future.

